Have you ever tried to learn how JavaScript Array Methods work couldn't grasp what it was all about? Or wished to do something with an array but struggled because you didn't know which one you needed?
If so, you're at the right place.
In JavaScript, arrays are list-like objects that possess many built-in methods. These methods allow you to perform operations that include adding or removing elements, find the index of a particular element, create a new string, and the list goes on.
This article aims to provide a guide of the most-used JavaScript array methods, based on what you need to do at first.
PermalinkMutate (modify) the original array
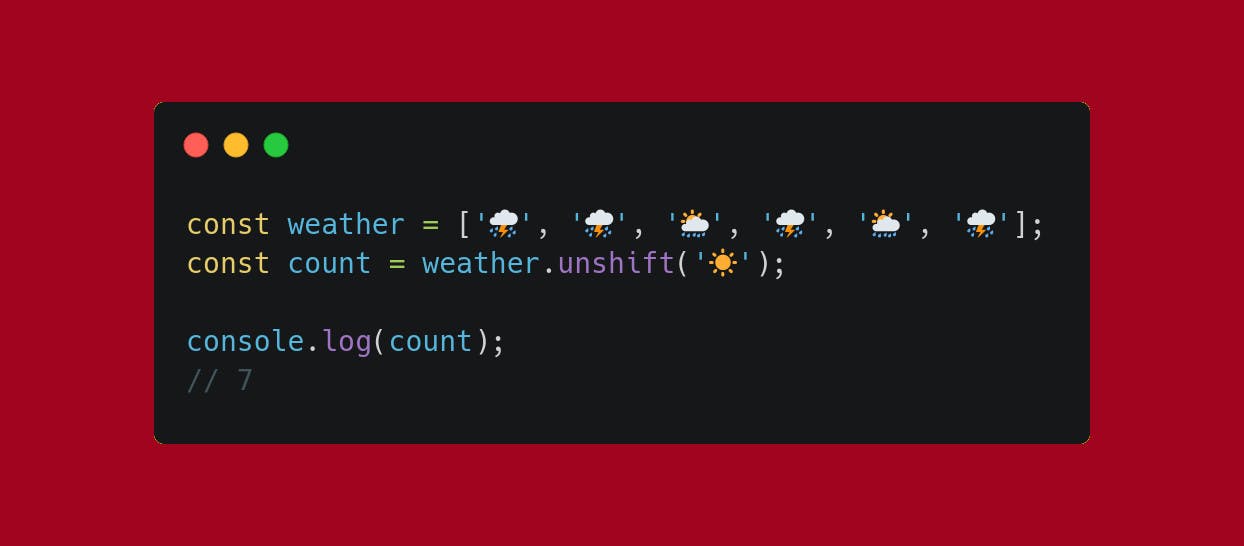
I want to add an element to the original array.
Use
.pushif you want it at the end of your arrayUse
.unshiftif you need it at the beginning


Beware, .push and .unshift return the array's new length.
Use .pop if you want to remove the one at the end, use .shift to remove the one at the start.


Just like .shift, .pop mutates (modifies) the original array.

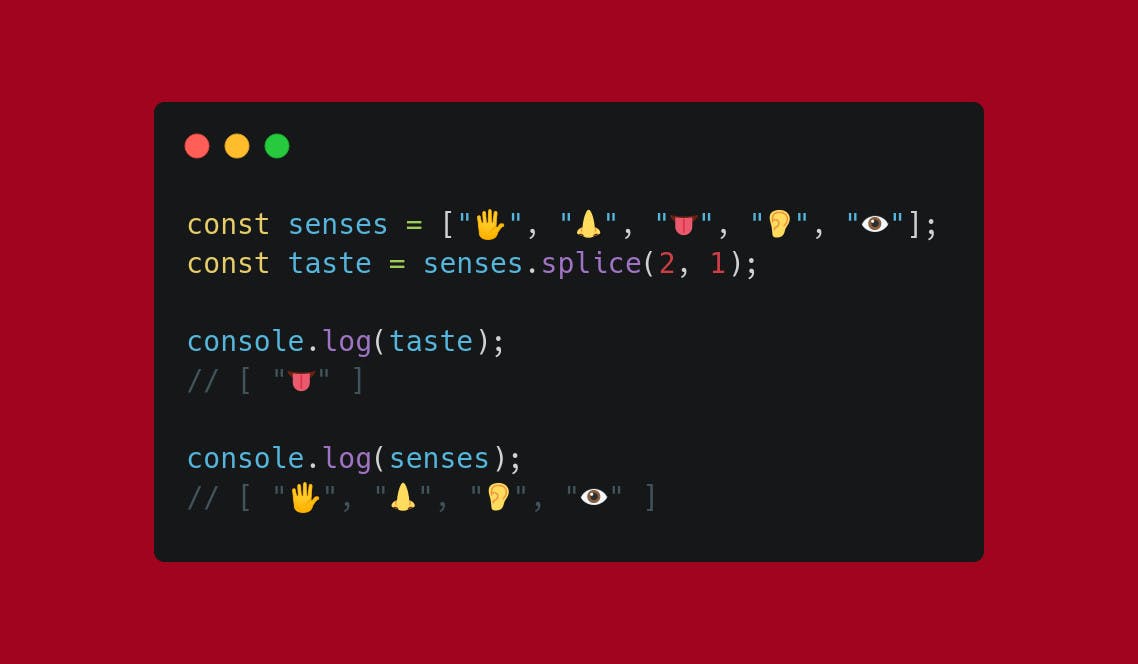
Use .splice to remove the one(s) you choose:
First parameter is the index at which you want to start
Second parameter (optional) is the number of elements to remove
Third element (optional) is (are) the element(s) to add instead
I want to do something else.
You can also use .reverse to reverse the position of your array's elements, use .sort to sort your elements (beware of this one as it compares UTF-16 code units values which can lead to unexpected results when comparing numbers), or use .fill to fill an array.
PermalinkCreate a new array
I want to compute it from the original array.
Use .map to loop over an array and create a new one. This method takes your array, apply the function you gave it on each element and return a new array. Very powerful.

I use the arrow function notation in the example above. If you don't know it, learn it there.
Here is how it works:
I stored 5 cyclists' energy into an array called
raceStartI created a new array called
summitI gave it the result of the
.mapmethod applied on theraceStartarrayI gave this
.mapmethod a function returning a simple calculationThis calculation will be executed on each element (
cyclistEnergywill take the value of the next element at every iteration)The results will fill the new array
Use .filter to create a new array based on a condition. It will test all elements of the original array and put those who passed the test into a new array.
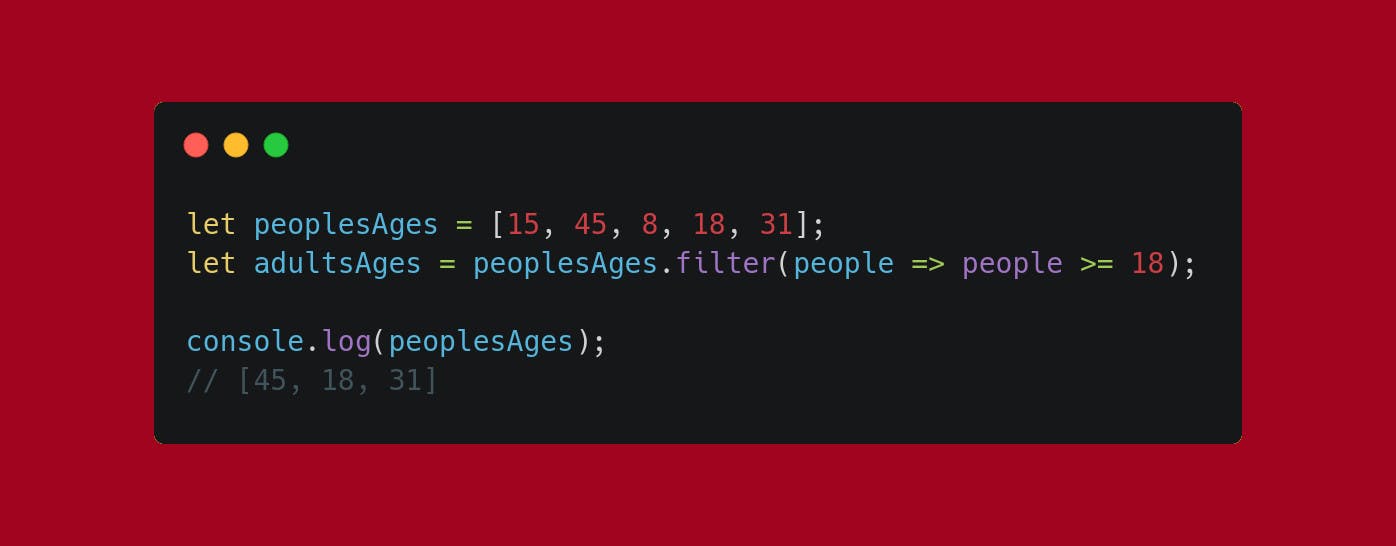
I stored 5 people's ages into an array
I gave to a new array the results from the
.filtermethod applied to thepeoplesAges' arrayI gave the method a function that returns only the elements below or equal to 18
The corresponding elements will fill the new array
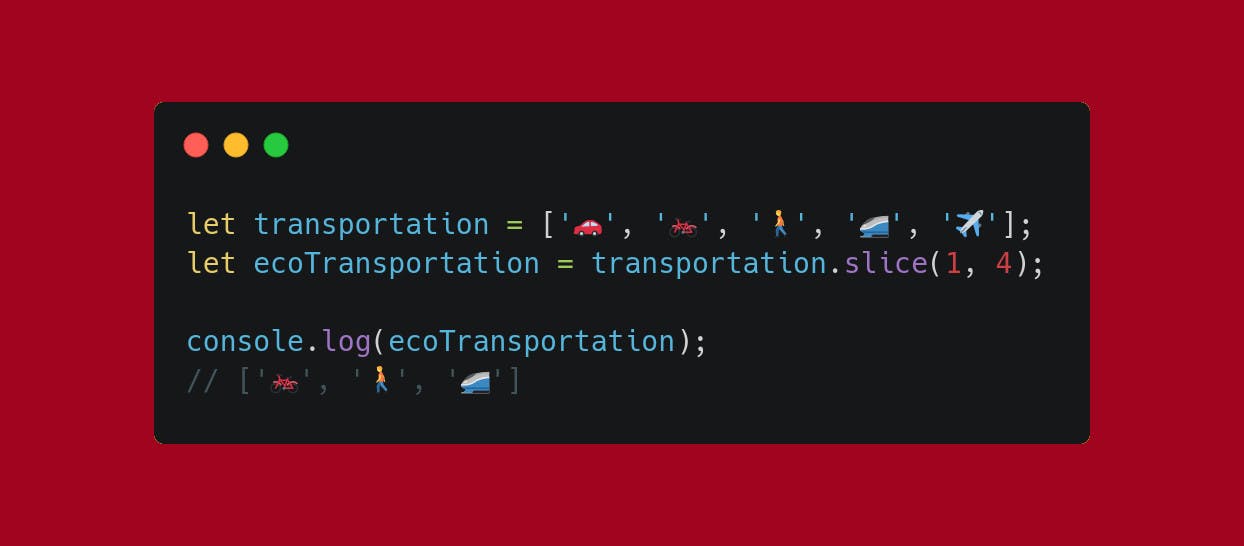
Use .slice to get just this. Pass starting and ending indexes as parameters and you're good to go.
Beware, the ending index is not included.
Use .concat on the original array and pass the array you want to add as parameter.
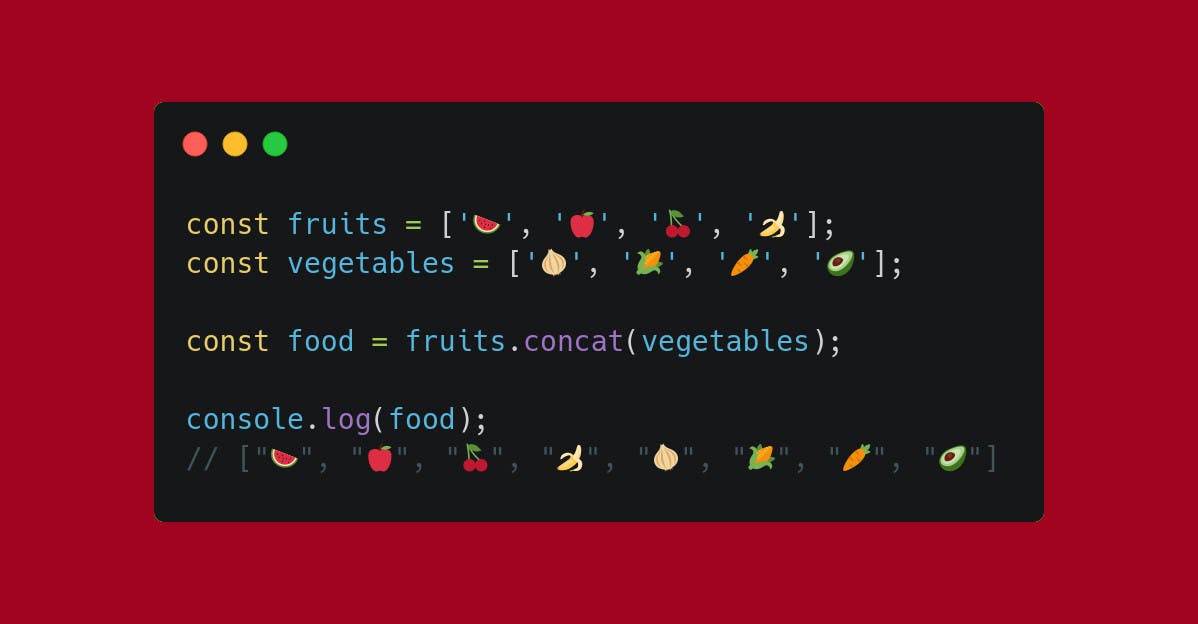
Use .flat or .flatMap.
.flat will flatten your array to one level of depth unless specified otherwise.

.flatMap just merges the .map and the .flat methods.
PermalinkFind an array index
... of a particular value.
Use .indexOf if you got the value and look for the index. Remember that indexes start at 0.
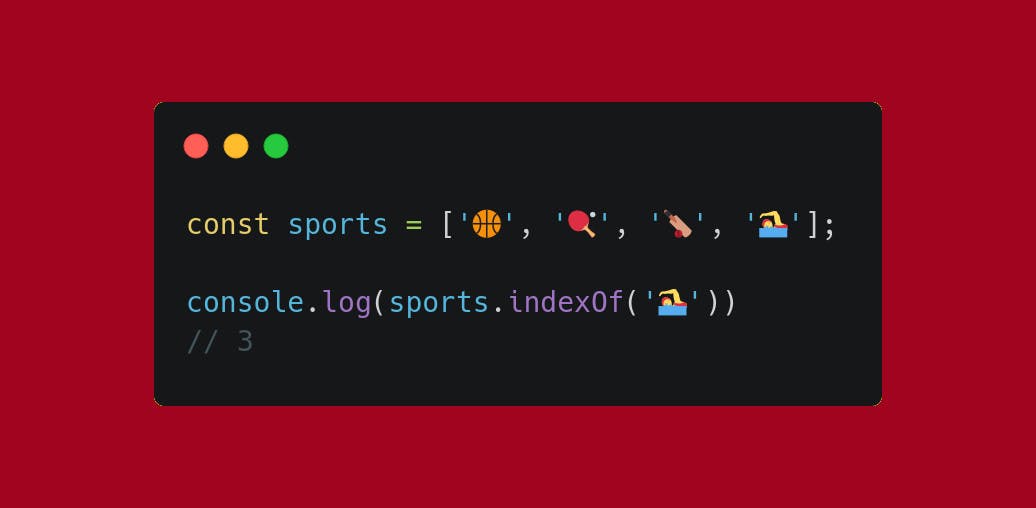
Use .findIndex if you only got the condition under which you want the element to be.

Beware, it will return the index only of the first element that satisfies the condition.
PermalinkFind an array element
Use .find. You need to pass it a function that will test each element of the array.
It works exactly like .findIndex except that it returns the first element itself instead of its index. Once again be careful as it returns only the first corresponding element.

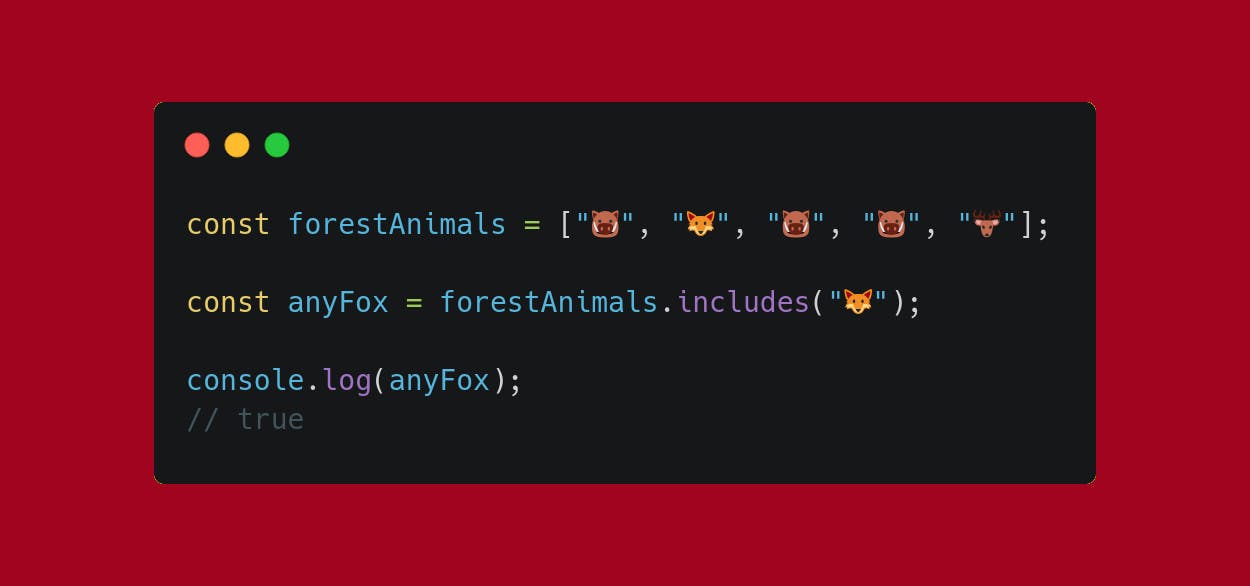
PermalinkKnow if my array includes...
... a particular value.
Use .includes.
Use .some or .every. The first will search for at least one specified element while the latter will test if every element satisfy a condition.
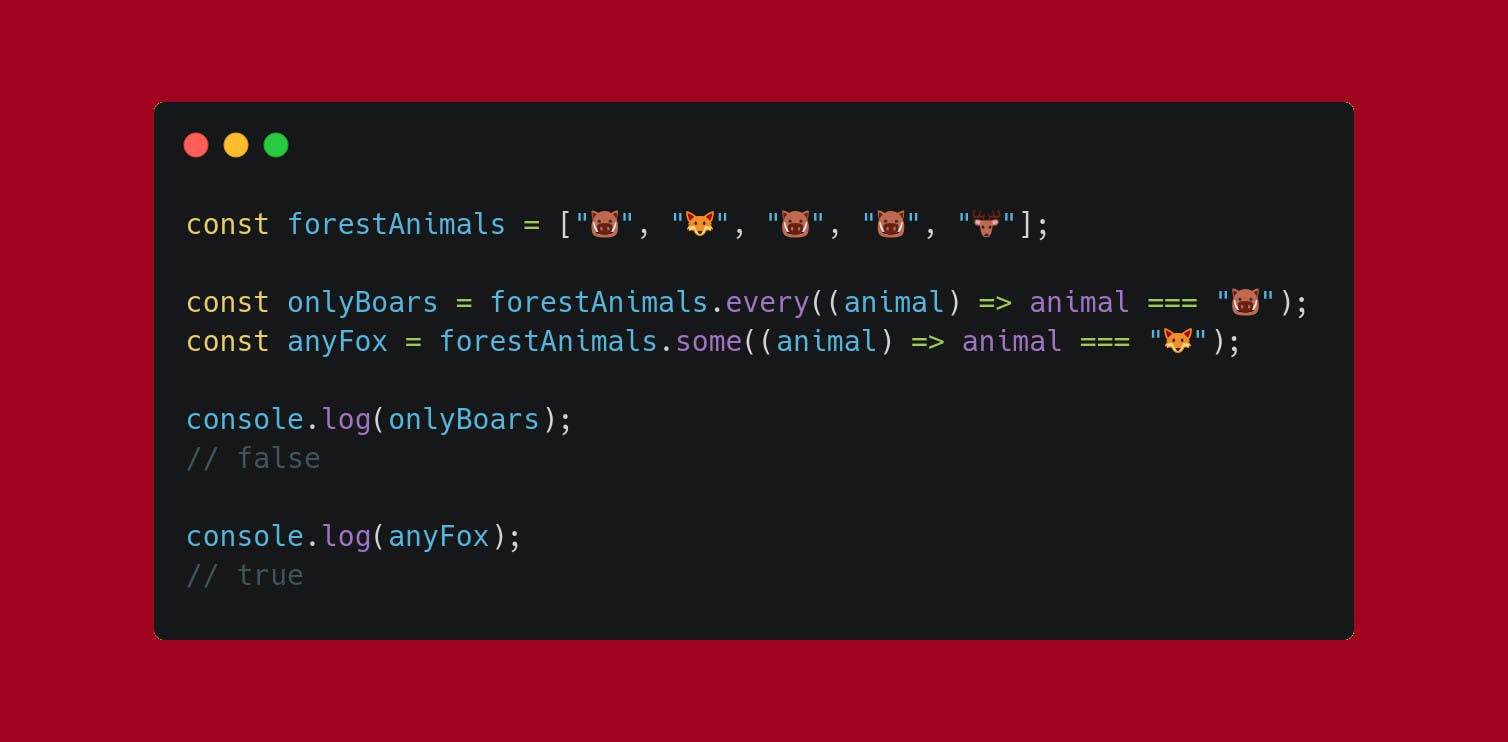
The console.log s in the above image read as follows:
Are there only boars in the
forestAnimalsarray? No.Is there any fox? Yes.
PermalinkCreate a new string
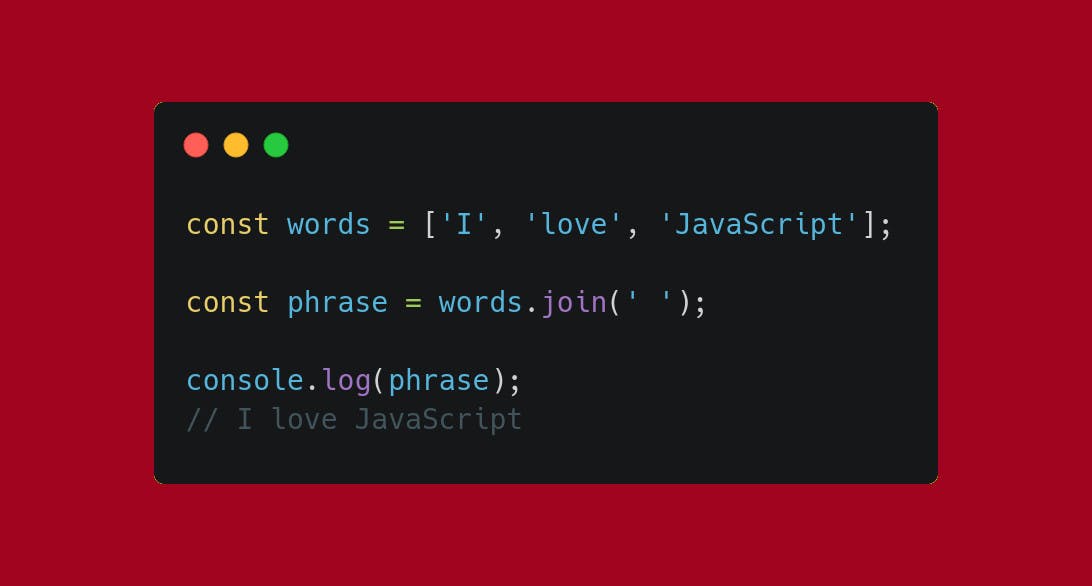
Use .join to join all the elements of an array into a string. You can specify a separator as a parameter, including a blank space.
PermalinkTransform to value
Use .reduce. This method deserves a little more attention.

As a first argument, it takes a callback function. As an optional second argument (not featured in the example), it takes an initial value.
The callback (also called "reducer") will execute an operation with two values: the previous value and the current value. Also super useful.
PermalinkLoop through an array
O.K. then. Use .forEach.

Once again, I used an arrow function here. Learn it there.
PermalinkDon't make that mistake
I plan on publishing many similar articles on Hashnode in the future. If you liked this article, consider ✅ following this blog (back to the top right corner) so you don't miss any!
It gives me superpowers and makes me want to write even more.
Also check out 🐦 my Twitter, where I write daily on web development and how to become a better learner.
